ДАВНО
ЗАБЫТОЕ СТАРОЕ
Дождливым
летом 2000-го года двое сотрудников ФТИ были приглашены в Токио на Первый
Японо-российский форум по высоким технологиям с "приглашенными"
докладами (см. статью "Великий форум" Японии и России" в Окне в Микромир, №1, 2000).
Японцы демонстрировали нам замечательные образцы
новейшей техники. С особой гордостью ими была продемонстрирована в токийском
представительстве фирмы PANASONIC электронная система жилища будущего, названная авторами "HII", что расшифровывалось как Home Information Infrastructure. Этой многокомнатной
квартире со стеклянными стенами авторы придавали особое значение и предрекали
ей особую роль в дальнейшем развитии информатики и электронной техники. И не
только. Речь шла о радикальном преображении человеческого быта, с одной
стороны, и о выходе промышленности на новый виток расширения производства
персональных компьютеров, с другой, да и о научно-техническом прогрессе вообще.
Как тут было не вспомнить о событиях конца 60-х - начала
70-х в Советском Союзе, когда аналогичная идея была – тоже в разовом порядке – осуществлена
и продемонстрирована в работе на Всесоюзной выставке достижений электроники
(проспект Вернадского, Москва, апрель 1970 г.). Устройство было названо
авторами ДИМ, или же Домашняя Информационная Машина, т.е. HIM, Home Information Machine, сравните с "HII".
Стоит ли подчеркивать, что происходило это задолго до появления персонального компьютера и Интернета, хотя содержало многие черты и того и другого, вместе взятых? Было получено на эту тему авторское свидетельство с приоритетом от 5 января 1971г. (А/с №375640, "Радиокомплекс", Р.П. Сейсян, М.Л. Выдревич, Б.Я. Смирнов и Ю.К. Якимов). А №1 журнала "Электронная промышленность" в 1972 г. (стр. 28-32) опубликовал статью Р.П. Сейсяна и М.Л. Выдревича "Что такое ДИМ?".
We have found possible to place here a
little bit reduced translation of the Russion version of the original paper in
Russian [«Electronnaya
promyshlennost’», vol. 27, №1, 1972, p.28-31] into English executed by J.E.Kitaev and
S.Markov to make it accessible to some English-speaking readers, in particular,
to HII (Home Information
Infrastructure)’s authors.
HIM, WHAT IS IT?
R.P. Seisyan, M.L.
Vydrevich
By 1963, the global fund of printed
production accumulated for the whole history of science has exceeded 108
items. Since then, not less than 5×104 of books and 8×104
of magazines appear annually [1]. In 1968, about 3×108 copies
of newspapers, 4.5×108 receivers and 1.5×108
TV distributed information daily to the world population [2]. Nevertheless, a
shortage of selected information chosen from the large flow and dispatched up
to a consumer in a concentrated rational form is felt.
An extremely fast growth of a bank
of the saved knowledge exceeds in its rates all known processes of public
development. Not without reason present stage of the development of mass media
is named as "the fourth revolution", comparing it on the importance
and social consequences with origin of language, appearance of written language
and invention of the book-printing. A simple expansion of information network
channels, increase of printed production etc., unfortunately, do not solve the
problem, since the ways of search and primary processing of necessary
information become more and more sophisticated. However, already now there are
strong grounds for believing that in relation with intensive development of
electronics, automatics and computer facilities an opportunity of wide use of
devices of automated search, processing and storing of the information shortly
will appear before long.
Will pass several years and the home
information machine become the same habitual subject of a life what watches,
telephone, tape recorder, record-player etc. are now.
To understand a history of
occurrence of creation idea of the home information machine, we shall afford a
small digression in the recent past of electronics.
As known, an advantage of integrated
circuits brought forth a necessity of a complete reconsideration of traditional
"discrete" electronics and the principles of designing of the
electron equipment. It is necessary to take into account, that the less are IC
element sizes at a given functional complexity, the higher is economic benefit
received from introduction of IC's. On the other hand, the assignment of a
number of components and units of traditional electronics is those that its
miniaturization can turn out inexpedient or even absurd. Therefore, in radio
and television equipment, independent units and blocks are classified not only
functional but also technological properties.
Such a design enables to replace
blocks in case of malfunction and supposes updating any of them independently.
The functionality of a traditional TV set can be considerably extended by the
use of increased integration-level ICs. So, for example, inserting into a block
of microcircuits the ICs of a sign generator as well as operative memory,
driving and synchronization devices, it is possible to receive on the screen a
text or sign display of the information coming from the board of management and
the RAM.
The home information machine is
intended for work in an independent mode, and at presence of the organized
cable network, as the peripheral information unit being the lowest part of the
large automated information system, constructed according to hierarchical
structure. The entrance device serving for communication with radio and
television channels, broadcasting and TV lines, provides switching of
information channels and carries out primary processing of the received
signals. Automated programmer serves for the management of the home information
machine under the given temporary program. It consists of the specifying
generator, frequency divider and executive devices.


For the experimental television
receiver, a block design is chosen. The block which carrying out the functions
of transformation and preliminary amplification of signals, as well as display
synchronization, is assembled from 12 integrated circuits. In the same block,
the bodies of control and adjustment of the television receiver are
concentrated. The TV tube, the loudspeaker, and the feed voltage source are represented
by separate blocks. The logics of development of a block design of the TV set
with application of ICs has resulted into an idea of creation of the home
information machine (HIM) representing a set of means of search, storage and
display a sign, audio and video information. The essentially new properties HIM
result from the inclusion in it of the operative and constant memory in the
logic block, multi channel universal information accumulator and universal
control board.
The keyboard is intended for manual
management of an information system. Such a board should solve a wide circle of
tasks of control and coding of the required or written down information. With
the help of keys, the address of necessary service provided with any functional
block of an information system is typed.
The logic block serves for an
imaging of the alphabetic or digital information on the screen. Sign generator
is represented by a constant memory on the diode matrixes. A row wise deviation
of a beam is used. The unlocking of a TV tube beam occurs only in those points,
which form the chosen sign. The control and synchronization circuits provide
synchronism of interrogation of a ROM matrix, and switching of a TV tube beam.
The operative memory is intended for
storing the entrance information subject to subsequent imaging on the screen.
The memory volume is determined by the amount of sign information, imaging in
one TV frame scan. For imaging of 800 marks in one frame scan, the RAM volume
should contain 5600 bits. The design of the RAMs on the shift registers
provides an opportunity of escalating of memory up to volume necessary for
imaging on the frame of many marks.
An opportunity of coinciding of the
considered sign information imaging system with one of the video information
reproduction, and opportunity of
reception on the screen both positive, and negative images of the sign
information is stipulated. For reproduction of the information can be used TV
tube, laser screen, holographic screen and any technical means allowing
receiving black-and-white or the color image the information.
The multi channel universal store of
the information, one of the most complex and problematic blocks, should be
designed for large volume of sound, code and video information, and the time of
the automated search on a code should not exceed several seconds. It is
necessary to take into account, that each second of the television program in
view of high quality of the image is estimated approximately in 106÷107
bits of the information, and the half-hour program contains 1010÷1011
bits that is equivalent of storing of 1000 volumes until 300 pages in everyone
of the textual information. At existing now tape or disk stores, the volume of
sign information can be not less than 107 signs. This means that the volume of
the audio programs can be not less than 200 hours, video programs not less than
20 hours.
The HIM development puts on agenda a
question on application of semi-conductor matrixes as textual cartridges of the
read-only memory allowing carrying out record and storage of short, but
frequently used information. In such cartridges, as in a notebook, it is
possible to keep the purely personal information, frequently used phone
numbers, and various rules, including the rule of the manipulation with the
home information machine. Electronic "library" from the read-only
memory based on diode and MOS matrixes, on CCD devices, on magnetic domains
ones etc. could be collected in parts for a long time.
The peripheral information devices
(user's HIM) allow establishing bilateral wire communication with information
storages. Thus, rational and accessible search language for information card
files becomes to be necessary [3]. Each peripheral device should have its own
number, similar to a telephone one.
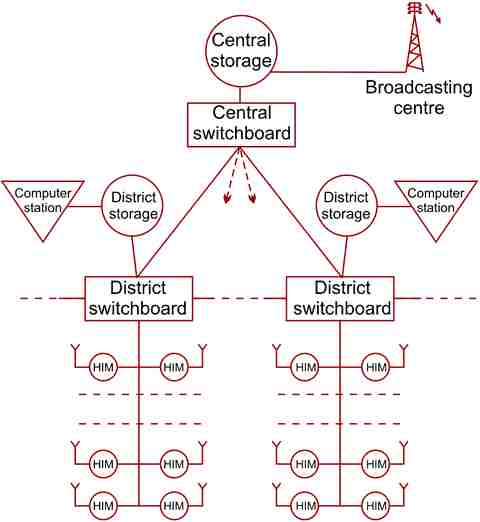
The communication within the limits
of a large information system will be carried out through regional and central
switchboards.
Let us consider some essentially new
information tasks solvable by the home information machine with the multi
channel universal information accumulator and bilateral communication line. The
complete or reduced texts of printed works and frequently used reference data,
educational programs can be kept in the multi channel universal information
accumulator and reproduced on the screen by a call of the subscriber. The
updating of the texts and reference data can be fulfilled by telephone or a
special channel with central (or regional) information item, and from any other
peripheral device. The data input in the accumulator is realized through the
control desk. The information kept in the memory of HIM by an appropriate set
of keys can be transferred automatically through regional or central
switchboards by communication channel in central and regional data storage or
in the memory of other peripheral device to appropriate user's number.
Similarly, it is possible to register telephone calls in the case of absence of
the subscriber, writing down the necessary information in the memory of the
machine connected to the communication line, to reproduce it then, having
connected HIM to radio, or television channel. The choice of the program, kept
in the store, can be carried out automatically through the control desk or
automated programmer. In the multi channel store, the various sorts of the
educational programs, advertising and information messages, as well as radio
and television programs can be preserved. The memory of stores will be capable
to keep significant volume of video and audio information.
Central and regional storages are
expedient to use for mathematical accounts, drawing up of the estimates, taking
of the electric meter readings for the centralized computer processing. It is
possible to carry out automatic transfer by digital codes of the distress
signals, fire and robbery ones using communication lines.
From this still not complete list of
tasks, one can judge how wide would be the application of the developed system
in a personal life. The block performance of the machine will allow steadily
increasing of its functionalities depending on the showed requirements.
The home information machine is a
functionally complex electronic device. It is possible to expect that a cost of
an electronic part of a HIM, in spite of a relative complexity of the circuit,
will not exceed the cost of similar electronic units incorporated into a
complex. It will be reduced systematically in connection with the constant
tendency to reduce a price of ICs, and also with improvement of a HIM design.
As a result of organization of HIM
mass production and creation of a wide information network, the time of search
and processing of the information will considerably decrease, the system of the
business relations will be simplified, the plenty of paper and consequently, of
such a valuable raw material as wood, will be saved, the polygraph manufacturing
will be reduced.
For creation of an information
complex, there is no necessity to solve any essentially new technical tasks.
Creation of VLSI, optoelectronics devices, and also the successes in the field
of magnetic and optical record of the information are the preconditions that,
in the coming decades, HIM will strongly enter into our life.

HIM can be used in the large
automated information system as a peripheral device. The basic links of the
system should become central and regional information stores, capable to keep
the large files of the information and working in a mode with division of time.
The basic information material should be kept in devices of long-term memory.
REFERENCES
1.
Nalimov V.V. Science-measurement,
M., "Science", 1969.
2.
Sukhotin A. A science and
information, M., "Mysl'", 1971.
3.
Kurbakov K.I. Coding and search in
the automatic dictionary. M., "Energy", 1968.
